WebSocket Connection Simplified: A Step-by-Step Guide
WebSocket technology enables real-time, bi-directional communication between users and servers, making it ideal for dynamic web applications. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of WebSocket, from understanding its headers to practical tips on establishing and managing real-time connections.

Setting Up a WebSocket Connection
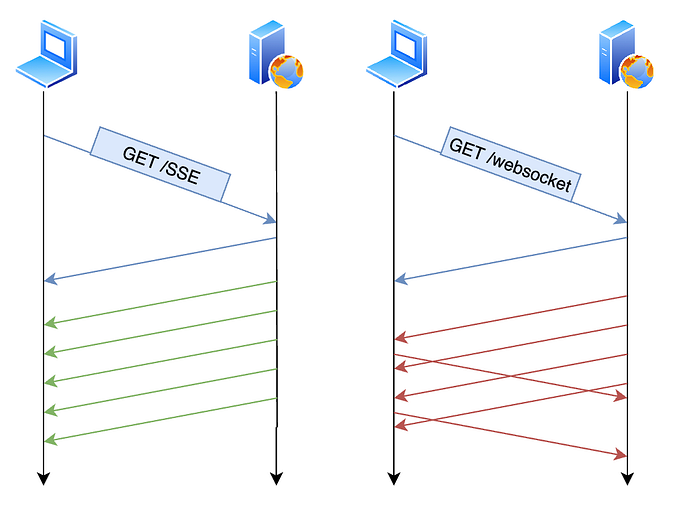
A WebSocket connection facilitates continuous, two-way data exchange over a persistent link, unlike the traditional HTTP request-response model. The WebSocket protocol allows both the client and server to send data independently without waiting for requests, making it highly efficient for real-time interactions.
Understanding WebSocket Headers
At the core of WebSocket communication is the unique handshake process, which involves a set of specialized headers. This handshake differs from standard HTTP headers and initiates the connection between the client and server.
For example, when a client connects to a WebSocket and requires authentication, it sends an upgrade request with an Authorization header. Below is a typical WebSocket handshake header example using Apidog:

Once the server receives and validates the request, it sends a response with its own headers, confirming the success of the handshake and establishing the connection.
Testing WebSocket APIs
WebSocket headers play a crucial role not only in setting up the connection but also in testing WebSocket APIs. A solid understanding of WebSocket exchanges will help you ensure that your APIs function correctly.
Tools like Apidog and Postman are invaluable for testing WebSocket APIs. These platforms provide user-friendly features for designing, managing, and verifying WebSocket interactions. Here’s how to use Apidog to streamline your WebSocket API testing process:
Step 1: Create a WebSocket Request
Open Apidog, click the “+” icon to start a new WebSocket API, and enter the target WebSocket URL.

Step 2: Configure WebSocket API Settings
Adjust parameters such as Params, Headers, and Cookies based on your authentication needs or specific requirements, and save the configuration.

Step 3: Establish the WebSocket Connection
Enter the URL in Apidog, click “Connect,” and watch as the handshake process initiates the real-time connection.

Troubleshooting WebSocket Connectivity Issues
If you encounter a “WebSocket Connection Failed” error, several factors could be at play. Network instability, SSL/TLS misconfigurations, server issues, mismatched protocols, security restrictions, bugs, CORS problems, or resource overloads may all affect WebSocket connectivity.
To troubleshoot these issues:
- Ensure a stable network
- Verify SSL/TLS settings
- Review server configurations
- Align protocols
- Update security measures
- Debug for errors
- Address CORS issues
- Optimize resources
For a more detailed guide on resolving these issues, explore WebSocket Connection Issues.